huawei network ekipmanlarında trafik istatiklerini toplamak
network ekipmanlarında trafik verisini toplamak genellikle üreticiye göre değişmekle birlikte ya pasif haldedir yada üreticinin belirlemiş olduğu bir değerlerle çalışmaktadır.
üreticiler veri toplama işi için ayrı bir mimari yapısı kullanmıyor / geliştirmediyse bu süreler genellikle sadece ev kullanıcısının işini yarayacaktır.
çünkü network ekipmanın üzerindeki arayüz sayısı fazla ve sürede kısa olursa cpu ve ram de ilave bir artışa neden olacaktır. bu nedenden dolayı sürelern kısaltılması öncesi cpu ve ram değerlerini takip etmek faydalı olacaktır.
huawei network ekipmanlarında arayüz altında
set flow-stat interval interval-timeile bu degeri değiştirebiliyorsunuz. buradaki interval-time 10 ile 600 arasında 10 katları olmak zorundadır. huaweinin bir çok ekipmanında varsayılan değeri 300 dur. huawei kritik veri gözlemlenmeyecek varsayılan degerlerde veya üstünde olmasını önermekte.
<Huawei> system-view
[Huawei] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
[Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] set flow-stat interval 4000/0/1 için 400 e set edelim ve arayüzün durumuna bakalım.
<Huawei> display interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 current state : UP
Line protocol current state : UP
Description:lineate-port-0
Switch Port, PVID : 1, TPID : 8100(Hex), The Maximum Frame Length is 9216
IP Sending Frames' Format is PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware address is 1047-80ac-cc60
Last physical up time : 2020-02-10 01:46:35 UTC+08:00
Last physical down time : 2020-02-10 01:46:30 UTC+08:00
Current system time: 2020-02-11 11:11:36+08:00
Port Mode: COMMON COPPER
Speed : 1000, Loopback: NONE
Duplex: FULL, Negotiation: ENABLE
Mdi : AUTO
Last 400 seconds input rate 80 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Last 400 seconds output rate 152 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Input peak rate 57064 bits/sec,Record time: 2020-02-10 07:43:17
Output peak rate 39872 bits/sec,Record time: 2020-02-11 11:11:36
Input: 71004 packets, 9224321 bytes
Unicast: 20023, Multicast: 49102
Broadcast: 1879, Jumbo: 0
Discard: 0, Total Error: 0
CRC: 0, Giants: 0
Jabbers: 0, Throttles: 0
Runts: 0, Alignments: 0
Symbols: 0, Ignoreds: 0
Frames: 0
Output: 20221 packets, 1679706 bytes
Unicast: 19989, Multicast: 0
Broadcast: 232, Jumbo: 0
Discard: 0, Total Error: 0
Collisions: 0, ExcessiveCollisions: 0
Late Collisions: 0, Deferreds: 0
Input bandwidth utilization threshold : 100.00%
Output bandwidth utilization threshold: 100.00%
Input bandwidth utilization : 0.01%
Output bandwidth utilization : 0.01%yukarıdaki çıktıda 400 saniyede bir örnekleme yapıldığı ve 90/152 bits/sec lik trafik olduğu görülmektedir.
Last 400 seconds input rate 80 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec Last 400 seconds output rate 152 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec huawei network ekipmanlarında alarm nedeniyle kapanmış olan arayüzlerin açılması
bir çok router ve switchte herhangi bir arayüz üzerindeki servislerde veya portta fiziksel hataların tespiti ile o arayüz üzerindeki servislerin / trafiğin daha fazla etkilenmemesi için arayüzü kapatabilirsiniz.
huawei network ekipmanlarında benzer şekilde kapatılmış arayüzlerin tespitini yapmak için farklı yöntemler mevcut.
display trapbuffer ve display logbuffer ile log incelemesi yapılabilir. display interface brief ile loop v.b. durumlar gözlemlenebilir.
en temel olanı ise arayüze doğrudan bakmak.
[test_router-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]display interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 current state : Port-alarm DOWN
Line protocol current state : DOWN
Link quality grade : --
Description:test-interface
Route Port,The Maximum Transmit Unit is 9212
Internet Address is 11.12.13.17/31
IP Sending Frames' Format is PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware address is bc3d-39ef-f236
The Vendor PN is MTRS-02X13-G
The Vendor Name is HG GENUINE
Port BW: 10G, Transceiver max BW: 10G, Transceiver Mode: SingleMode
WaveLength: 1310nm, Transmission Distance: 10km
Rx Power: -2.09dBm, Warning range: [-14.40, 0.50]dBm
Tx Power: -40.00dBm, Warning range: [-8.20, 0.50]dBm
Loopback:none, LAN full-duplex mode, Pause Flowcontrol:Receive Enable and Send Enable
Last physical up time : 2020-08-22 14:27:21 UTC+03:00
Last physical down time : 2020-08-22 14:27:23 UTC+03:00
Current system time: 2020-08-22 17:31:33+03:00
Statistics last cleared:2020-08-22 16:32:36
Last 10 seconds input rate: 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Last 10 seconds output rate: 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Input: 0 bytes, 0 packets
Output: 0 bytes, 0 packets
Input:
Unicast: 0 packets, Multicast: 0 packets
Broadcast: 0 packets, JumboOctets: 0 packets
CRC: 0 packets, Symbol: 0 packets
Overrun: 0 packets, InRangeLength: 0 packets
LongPacket: 0 packets, Jabber: 0 packets, Alignment: 0 packets
Fragment: 0 packets, Undersized Frame: 0 packets
RxPause: 0 packets
Output:
Unicast: 0 packets, Multicast: 0 packets
Broadcast: 0 packets, JumboOctets: 0 packets
Lost: 0 packets, Overflow: 0 packets, Underrun: 0 packets
System: 0 packets, Overrun: 0 packets
TxPause: 0 packets
Unknown Vlan: 0 packets
Input bandwidth utilization : 0%
Output bandwidth utilization : 0%veya
[test_router-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]display interface phy-option GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Port Physical Status :DOWN
Physical Down Reason :PORT_ALARM_DOWN
Loopback :none
Duplex mode :full-duplex
Pause Flowcontrol:
Receive :Enable
Send :Enable
SFP imformation:
The Vendor PN is MTRS-02X13-G
The Vendor Name is HG GENUINE
Port BW: 10G, Transceiver max BW: 10G, Transceiver Mode: SingleMode
WaveLength: 1310nm, Transmission Distance: 10km
Rx Power: -2.08dBm, Warning range: [-14.40, 0.50]dBm
Tx Power: -40.00dBm, Warning range: [-8.20, 0.50]dBmyukarıdaki örneklerde
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 current state : Port-alarm DOWN
Tx Power: -40.00dBm, Warning range: [-8.20, 0.50]dBm
Port Physical Status :DOWN
Physical Down Reason :PORT_ALARM_DOWNarayüzün alarm nedeniyle down olduğu ve doğal olarak tx = -40 olduğu görülmektedir.
bu örnekte arayüz altında hata olmadığı görülüyor. alarmlar temizlenmiş v.b. olabilir. arayüzün neden kapanmış olduğuna bakalım.
[test_router-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]display port-error-info interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 port-error information
================================================================================
input-error | output-error
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
trap enable : Yes | trap enable : Yes
trigger down : No | trigger down : No
alarm status : No | alarm status : No
threshold high : 1000 | threshold high : 1000
threshold low : 100 | threshold low : 100
interval : 10 sec. | interval : 10 sec.
stat(h) : 0 | stat(h) : 0
stat(l) : 0 | stat(l) : 0
================================================================================
crc-error | symbol-error
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
trap enable : Yes | trap enable : Yes
trigger down : Yes | trigger down : No
alarm status : No | alarm status : No
threshold high : 3 | threshold high : 1000
threshold low : 3 | threshold low : 100
percent : 0 | N/A : N/A
interval : 10 sec. | interval : 10 sec.
stat(h) : 0 | stat(h) : 0
stat(l) : 0 | stat(l) : 0
[test_router-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]arayüz için 4 alarm kontrolün aktif olduğu görülmektedir. çıktıya baktığımızda
crc-error
trap enable : Yes
trigger down : Yes crc hataları nedeniyle tetiklendiği görülmektedir. ilk önce portun kapanmasına neden olan alarmlar giderilmeli. alarm nedeni giderildikten sonra yapılması gereken için port üzerindeki alarmların clear edilmesi gerekmekte.
bunun nasıl yapılacağını
huawei routerlarda interface üzerinde alarm sayısını sıfırlama
başlıklı yazıda yazmıştım. alarmları sıfırladıktan sonra arayüzün aktif hala gelmesi gerekiyor. eğer aktif olmaz ise portu restart yapmak faydalı olabilir.
[test_router-GigabitEthernet1/0/1]restartRIPE NCC Training Course Material
Latest version: 20190815
Table of Contents
- LIR Training Course
This is a one-day introduction to the RIPE NCC administrative procedures and RIPE Policies related to obtaining and distributing Internet number resources (i.e. IP addresses, AS Numbers), operating a Local Internet Registry (LIR) and working with the RIPE Database. - RIPE Database Training Course
This one-day course will teach you how to use the RIPE Database like a pro. Using a combination of hands-on activities with theory, you will get a comprehensive idea of what the RIPE Database is and what you can do with it. - Basic IPv6 Training Course
This one-day course will teach you about the need for IPv6 and provide you with basic information about how to start planning your deployment. - Advanced IPv6 Training Course
This is a two-day practical course about IPv6 technical details, including dynamic protocols such as OSPF and BGP. - IPv6 Security Training Course
This one-day course provides an overview of the most relevant IPv6 security topics. You will gain insight into industry best practice and gain a high-level understanding of the most pressing IPv6 security concerns today. - BGP Operations and Security Training Course
This one-day course offers an in-depth look into Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). After this course, you will be capable of reinforcing theory through practice with our interactive exercises following each topic. - DNSSEC Training Course
This is a one-day practical training course that will teach you how DNSSEC works and the related procedures and tools.
- Measurements and Tools Training Course
This one-day introductory hands-on course will teach you the basics of RIPEstat and RIPE Atlas. - Additional information
Here you will find a list of useful links.
Training Courses
Local Internet Registry (LIR) Training Course
RIPE Database Training Course
Basic IPv6 Training Course
- Course Slides
- Training Exercise: Addressing Plan with Possible Solutions
- Training Exercise: IPv6 Address Notation Solution
- IPv6 Address Types
- IPv6 Subnetting Card
Advanced IPv6 Training Course
IPv6 Security Training Course
BGP Operations and Security Training Course
- Course Overview
- Course Slides
- Course Laboratories Appendix
- Course Database Objects Appendix
- Route Object Creation Flowchart
Additional references (External links)
- BGP:
- A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (RFC-4271)
- Multiprotocol Extensions for BGP-4 (RFC-4726)
- BGP-4 Implementation Report (RFC-4276)
- Experience with the BGP-4 Protocol (RFC-4277)
- Capabilities Advertisement with BGP-4 (RFC-2842)
- BGP Communities Attribute (RFC-1997)
- BGP Extended Communities Attribute (RFC-4360)
- BGP Route Reflection (RFC-4456)
- RIPE Database:
- RPSL:
- Routing Policy Specification Language (RFC-2622)
- Routing Policy System Security (RFC-2725)
- Using RPSL in Practice (RFC-2650)
- Recomendations on IPv4 Route Aggregations
- An Application of the BGP Community Attribute in Multi-home Routing (RFC 1998)
- Routing Policy Specification Language next generation (RFC 4012)
- Routing Information Service Project
- Routing Registry Consistency Project
- Resource Certification:
DNSSEC Training Course
Measurements and Tools Training Course
(covering RIPEstat and RIPE Atlas)
- Course Overview
- Course Slides
- Course Exercises
- Course Exercises Solutions
- Course Slides in Keynote format (with additional notes and explanations)
- Course Slides in PowerPoint format
Additional Information
All material is provided by the RIPE NCC under 2-Clause BSD License.Created: 31 Dec 2010 – Last updated: 27 Aug 2019 “” TRAINING
Huawei Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) Technology White Paper
huawei ağ ekipmanlarında basit martini vpls uygulaması
aşağıdaki topoloji üzerinde huawei ağ ekipmanlarını kullanarak basit bir mpls martini vpls örneği yapalım.
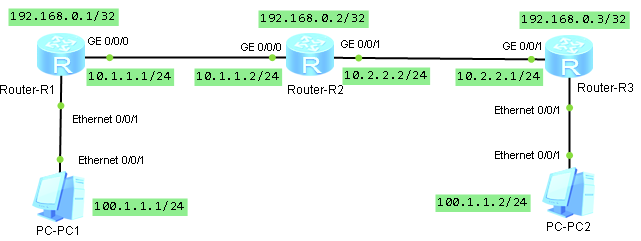
öncelikle loopback ve ip tanımlarını sırasıyla yapalım.
sysname R1
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
interface LoopBack0
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.255sysname R2
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
interface LoopBack0
ip address 192.168.0.2 255.255.255.255sysname R3
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0
interface LoopBack0
ip address 192.168.0.3 255.255.255.255tüm arayüzler aktif olduktan sonra örnekte ospf yönlendirme protokolünü kullanacağımız için yönlendiriciler üzerinde ospf leri aktif etmek için gerekli yapılandırmasını yapalım.
sysname R1
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255sysname R2
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 192.168.0.2 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255sysname R3
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.0.3 0.0.0.0ospf de aktif olduktan sonra mpls tanımlarına başlayabiliriz. tüm yönlendiriciler de global de mpls i aktif edelim.
mpls lsr-id 192.168.0.x
mpls
mpls l2vpn
mpls ldpsonrasında ağımızda yönlendiriciler arasındaki arayüz bağlantıları altında mpls, mpls ldp aktif ediyoruz.
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/x
mpls
mpls ldpen temel kontrolleri yaptık bir sorun görülmüyor. şimdi pc1 – pc2 arasındaki haberleşmenin sağlanması için gerekli yapılandırmaya sıra geldi. öncelikle r1 den r3 , r3 den r1 doğru ldp remote tanımlarını yapmalıyız.
sysname R1
mpls ldp remote-peer ldp_peer_to_r3
remote-ip 192.168.0.3sysname R3
mpls ldp remote-peer ldp_peer_to_r1
remote-ip 192.168.0.1şimdi yapabileceğimiz bazı kontrolleri yapalım.
<R1>display mpls interface
Interface Status TE Attr LSP Count CRLSP Count Effective MTU
GE0/0/0 Up Dis 4 0 1500
<R1><R1>display mpls ldp session
LDP Session(s) in Public Network
Codes: LAM(Label Advertisement Mode), SsnAge Unit(DDDD:HH:MM)
A '*' before a session means the session is being deleted.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PeerID Status LAM SsnRole SsnAge KASent/Rcv
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.0.2:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:01:45 423/423
192.168.0.3:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:01:53 455/455
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
TOTAL: 2 session(s) Found.[R1]display mpls route-state
Codes: B(BGP), I(IGP), L(Public Label BGP), O(Original BGP), U(Unknow)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dest/Mask Next-Hop Out-Interface State LSP VRF Type
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.0.1/32 127.0.0.1 InLoop0 READY 1 0 I
192.168.0.2/32 10.1.1.2 GE0/0/0 READY 2 0 I
192.168.0.3/32 10.1.1.2 GE0/0/0 READY 2 0 I[R1]display mpls lsp
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LSP Information: LDP LSP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name
192.168.0.2/32 NULL/3 -/GE0/0/0
192.168.0.2/32 1028/3 -/GE0/0/0
192.168.0.3/32 NULL/1025 -/GE0/0/0
192.168.0.3/32 1029/1025 -/GE0/0/0
192.168.0.1/32 3/NULL -/- şimdi vsi ları oluşturalım. burada dikkat edilmesi gereken en önemli nokta vsi-id lerin aynı olması gerektiğidir.
sysname R1
vsi vsi_for_pc static
pwsignal ldp
vsi-id 100
peer 192.168.0.3sysname R3
vsi vsi_for_pc static
pwsignal ldp
vsi-id 100
peer 192.168.0.1son aşamaya gelmiş olduk. bilgisayarların bağlı arayüzler için tanımları da tapalım.
sysname R1
interface Ethernet0/0/1
l2 binding vsi vsi_for_pcsysname R3
interface Ethernet0/0/1
l2 binding vsi vsi_for_pctüm yapılandırmaları tamamlamış olduk. şimdi bilgisayarlara ip leri girerek erişim kontrolleri yapalım. bilgisayarlarda ağ geçidi olarak karşı bilgisayarın iplerini girelim.
PC>ping 100.1.1.2
Ping 100.1.1.2: 32 data bytes, Press Ctrl_C to break
From 100.1.1.2: bytes=32 seq=1 ttl=128 time=94 ms
From 100.1.1.2: bytes=32 seq=2 ttl=128 time=156 ms
From 100.1.1.2: bytes=32 seq=3 ttl=128 time=62 ms
From 100.1.1.2: bytes=32 seq=4 ttl=128 time=94 ms
From 100.1.1.2: bytes=32 seq=5 ttl=128 time=110 ms
--- 100.1.1.2 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 62/103/156 msyönlendiricilere ait yapılandırmaların tam hali aşağıda yer almaktadır.
sysname R1
mpls lsr-id 192.168.0.1
mpls
mpls l2vpn
mpls ldp
vsi vsi_for_pc static
pwsignal ldp
vsi-id 100
peer 192.168.0.3
mpls ldp remote-peer ldp_peer_to_r3
remote-ip 192.168.0.3
interface Ethernet0/0/1
l2 binding vsi vsi_for_pc
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
mpls
mpls ldp
interface LoopBack0
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.255
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255sysname R2
mpls lsr-id 192.168.0.2
mpls
mpls ldp
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
mpls
mpls ldp
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
mpls
mpls ldp
interface LoopBack0
ip address 192.168.0.2 255.255.255.255
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 192.168.0.2 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255sysname R3
mpls lsr-id 192.168.0.3
mpls
mpls l2vpn
mpls ldp
vsi vsi_for_pc static
pwsignal ldp
vsi-id 100
peer 192.168.0.1
mpls ldp remote-peer ldp_peer_to_r1
remote-ip 192.168.0.1
interface Ethernet0/0/1
l2 binding vsi vsi_for_pc
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0
mpls
mpls ldp
interface LoopBack0
ip address 192.168.0.3 255.255.255.255
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.0.3 0.0.0.nokia sros için araçlar
genel olarak network ekipmanlarında cli ile konfigürasyon yapıyorsanız sıklıkla kopyala – yapıştır yapıyorsunuzdur. ancak bu yöntem hatalara oldukça açıktır.
bu hatayı minimize etmek adına python ile yazılmış nokia sros güzel bir kod bulmuştum. bunu paylaşmak istedim. örnek için aşağıdaki şekilde bir konfigürasyonumuz olsun.. bunu c1.txt olarak kaydediyoruz.
vpls 11 customer 1 vpn 11 i-vpls create
backbone-vpls 100:11
exit
stp
shutdown
exit
sap 1/5/1:11 create
exit
sap 1/5/1:12 create
exit
no shutdown
exit
vpls 100 customer 1 vpn 100 b-vpls create
service-mtu 2000
stp
shutdown
exit
mrp
flood-time 10
no shutdown
exit
sap 1/5/1:100 create
exit
spoke-sdp 3101:100 create
exit
spoke-sdp 3201:100 create
exit
no shutdown
exitt.py olarak kaydettiğimiz python kodunu çalıştığımızda mevcut kodumuz aşağıdaki örnekte görüleceği üzere yeniden düzenleniyor. bu şekilde bir yapı bir çok olası hatanın önüne geçecektir.
fcicek@cicek:~/mpls/sros$ python t.py c1.txt
/configure vpls 11 customer 1 vpn 11 i-vpls create backbone-vpls 100:11
/configure vpls 11 customer 1 vpn 11 i-vpls create stp shutdown
/configure vpls 11 customer 1 vpn 11 i-vpls create sap 1/5/1:11 create
/configure vpls 11 customer 1 vpn 11 i-vpls create sap 1/5/1:12 create
/configure vpls 11 customer 1 vpn 11 i-vpls create no shutdown
/configure vpls 100 customer 1 vpn 100 b-vpls create service-mtu 2000
/configure vpls 100 customer 1 vpn 100 b-vpls create stp shutdown
/configure vpls 100 customer 1 vpn 100 b-vpls create mrp flood-time 10
/configure vpls 100 customer 1 vpn 100 b-vpls create mrp no shutdown
/configure vpls 100 customer 1 vpn 100 b-vpls create sap 1/5/1:100 create
/configure vpls 100 customer 1 vpn 100 b-vpls create spoke-sdp 3101:100 create
/configure vpls 100 customer 1 vpn 100 b-vpls create spoke-sdp 3201:100 create
/configure vpls 100 customer 1 vpn 100 b-vpls create no shutdownkullanılan t.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import re
import math
import sys
def pop(stack):
try:
stack.pop()
except Exception as err:
print("ERROR: Unable to flush stack - %s" %err)
def output(stack):
output = " ".join(stack)
print(output)
return output
def sros_flatten(data):
stack = []
exit_detected = False
indent = 0
new_conf = ""
for line in data.lstrip().splitlines():
l = len(line) - len(line.lstrip())
nxt_indent = math.ceil(float(l/4))
if line.startswith(("#", "echo")) or line.strip() == "":
pass
elif line.strip() == "exit all":
new_conf = new_conf + "\n" + output(stack)
else:
if nxt_indent == 0 and line.strip() == "configure":
new_line = str("/") + str(line.strip())
stack.append(new_line)
elif nxt_indent > indent:
if line.strip() != "configure" and len(stack) == 0:
stack.insert(0, "/configure")
stack.append(line.lstrip())
elif nxt_indent == indent:
if line.strip() != "exit":
if exit_detected:
stack.append(line.strip())
else:
if len(stack) != 0:
new_conf = new_conf + "\n" + output(stack)
pop(stack)
stack.append(line.strip())
else:
stack.insert(0, "/configure")
stack.append(line.strip())
exit_detected = False
else:
if line.strip() == "exit":
if not exit_detected:
new_conf = new_conf + "\n" + output(stack)
del stack[-2:]
else:
pop(stack)
exit_detected = True
else:
new_conf = new_conf + "\n" + output(stack)
exit_detected = False
pop(stack)
indent = nxt_indent
return new_conf
def main():
filename = sys.argv[1]
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
data = f.read()
sros_flatten(data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()